Federal Reserve Economic Data: Your trusted data source since 1991
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
NOTES
Source: Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
Release: Failures and Assistance Transactions
Units: Number of Institutions, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Annual
Notes:
Transaction Types
Institutions have been resolved through several different types of transactions. The transaction types outlined below can be grouped into three general categories, based upon the method employed to protect insured depositors and how each transaction affects a failed/assisted institution's charter. In most assistance transactions, insured and uninsured depositors are protected, the failed/assisted institution remains open and its charter survives the resolution process. In purchase and assumption transactions, the failed/assisted institution's insured deposits are transferred to a successor institution, and its charter is closed. In most of these transactions, additional liabilities and assets are also transferred to the successor institution. In payoff transactions, the deposit insurer - the FDIC or the former Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation - pays insured depositors, the failed/assisted institution's charter is closed, and there is no successor institution. For a more complete description of resolution transactions and the FDIC's receivership activities, see Managing the Crisis: The FDIC and RTC Experience, a study prepared by the FDIC's Division of Resolutions and Receiverships. Copies are available from the FDIC's Public Information Center.
Category 1 Institution's charter survives
A/A Assistance Transactions. These include:
1) transactions where assistance was provided to the acquirer, who purchased the entire institution. For a few FSLIC transactions, the acquirer purchased the entire bridge bank - type entity, but certain other assets were moved into a liquidating receivership prior to the sale, and
2) open bank assistance transactions, including those where assistance was provided under a systemic risk determination (in such cases any costs that exceed the amounts estimated under the least cost resolution requirement would be recovered through a special assessment on all FDIC-insured institutions).
REP Reprivatization, management takeover with or without assistance at takeover, followed by a sale with or without additional assistance.
Category 2 Institution's charter is terminated, insured deposits plus some assets and other liabilities are transferred to a successor charter
P&A Purchase and Assumption, where some or all of the deposits, certain other liabilities and a portion of the assets (sometimes all of the assets) were sold to an acquirer. It was not determined if all of the deposits (PA) or only the insured deposits (PI) were assumed.
PA Purchase and Assumption, where the insured and uninsured deposits, certain other liabilities and a portion of the assets were sold to an acquirer.
PI Purchase and Assumption of the insured deposits only, where the traditional P&A was modified so that only the insured deposits were assumed by the acquiring institution.
IDT Insured Deposit Transfer, where the acquiring institution served as a paying agent for the insurer, established accounts on their books for depositors, and often acquired some assets as well. Includes ABT (asset-backed transfer, a FSLIC transaction that is very similar to an IDT).
MGR An institution where FSLIC took over management and generally provided financial assistance. FSLIC closed down before the institution was sold.
Category 3 PO Payout, where the insurer paid the depositors directly and placed the assets in a liquidating receivership.
Note: Includes transactions where the FDIC established a Deposit Insurance National Bank to facilitate the payout process.
For additional notes, see https://www5.fdic.gov/hsob/HSOBNotes.asp#BF1.
Suggested Citation:
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, Failures of all Institutions for the United States and Other Areas [BKFTTLA641N], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/BKFTTLA641N, May 15, 2024.
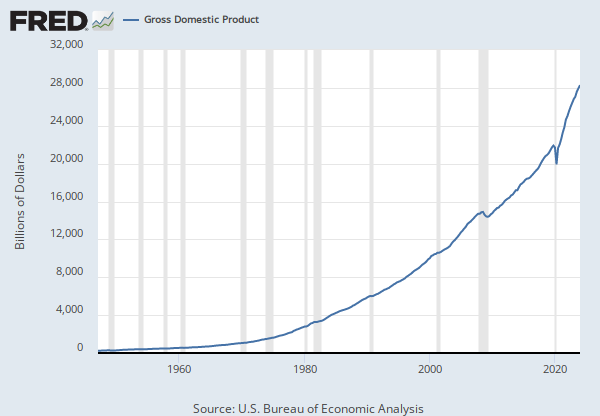
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Release: Gross Domestic Product
Units: Billions of Chained 2017 Dollars, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate
Frequency: Quarterly
Notes:
BEA Account Code: A191RX
Real gross domestic product is the inflation adjusted value of the goods and services produced by labor and property located in the United States.For more information see the Guide to the National Income and Product Accounts of the United States (NIPA). For more information, please visit the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Suggested Citation:
U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Real Gross Domestic Product [GDPC1], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/GDPC1, May 15, 2024.
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US)
Release: Z.1 Financial Accounts of the United States
Units: Billions of Dollars, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Quarterly, End of Period
Notes:
Source ID: FL894104005.Q
For more information about the Flow of Funds tables, see the Financial Accounts Guide.
With each quarterly release, the source may make major data and structural revisions to the series and tables. These changes are available in the Release Highlights.
In the Financial Accounts, the source identifies each series by a string of patterned letters and numbers. For a detailed description, including how this series is constructed, see the series analyzer provided by the source.
Suggested Citation:
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), All Sectors; Debt Securities and Loans; Liability, Level [TCMDO], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/TCMDO, May 15, 2024.
RELEASE TABLES
- Table 1.1.6. Real Gross Domestic Product, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.2.6. Real Gross Domestic Product by Major Type of Product, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.3.6. Real Gross Value Added by Sector, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.4.6. Relation of Real Gross Domestic Product, Real Gross Domestic Purchases, and Real Final Sales to Domestic Purchasers, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.5.6. Real Gross Domestic Product, Expanded Detail, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.7.6. Relation of Real Gross Domestic Product, Real Gross National Product, and Real Net National Product, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.8.6. Command-Basis Real Gross Domestic Product and Gross National Product, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
- Table 1.17.6. Real Gross Domestic Product, Real Gross Domestic Income, and Other Major NIPA Aggregates, Chained Dollars: Quarterly
RELATED DATA AND CONTENT
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Other Formats
Real Gross Domestic Product
Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Quarterly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Index 2017=100, Quarterly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change from Preceding Period, Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change from Preceding Period, Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate Percent Change from Quarter One Year Ago, Quarterly, Not Seasonally Adjusted Percent Change from Quarter One Year Ago, Quarterly, Seasonally AdjustedAll Sectors; Debt Securities and Loans; Liability, Level
Millions of Dollars, Annual, Not Seasonally Adjusted